release time:2021-08-31 13:54:08
Biochemistry analyzers, belong to the category of clinical diagnostic analyzers. Biochemistry analyzer is a test device used to test human liver function, kidney function, blood glucose, blood lipids, cardiac enzymes and ions and other testing items. Biochemistry analyzers generally use venous blood as the test sample to determine potential human diseases through the testing of the above items.
The third generation of biochemical analyzer is fully automatic biochemical analyzer. Fully automatic biochemical analyzer from the sample to the results of the whole process is completely automated by the instrument. The operator only needs to put the sample on the specific position of the biochemical analyzer and choose the program to start the instrument to take the test report.
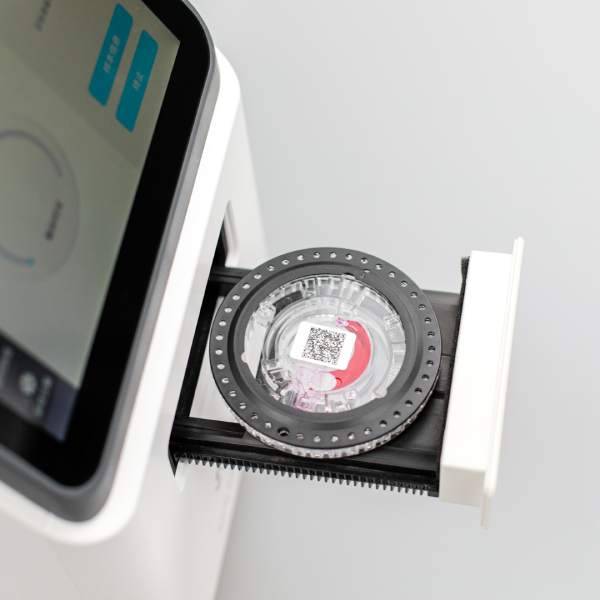
2022-09-15
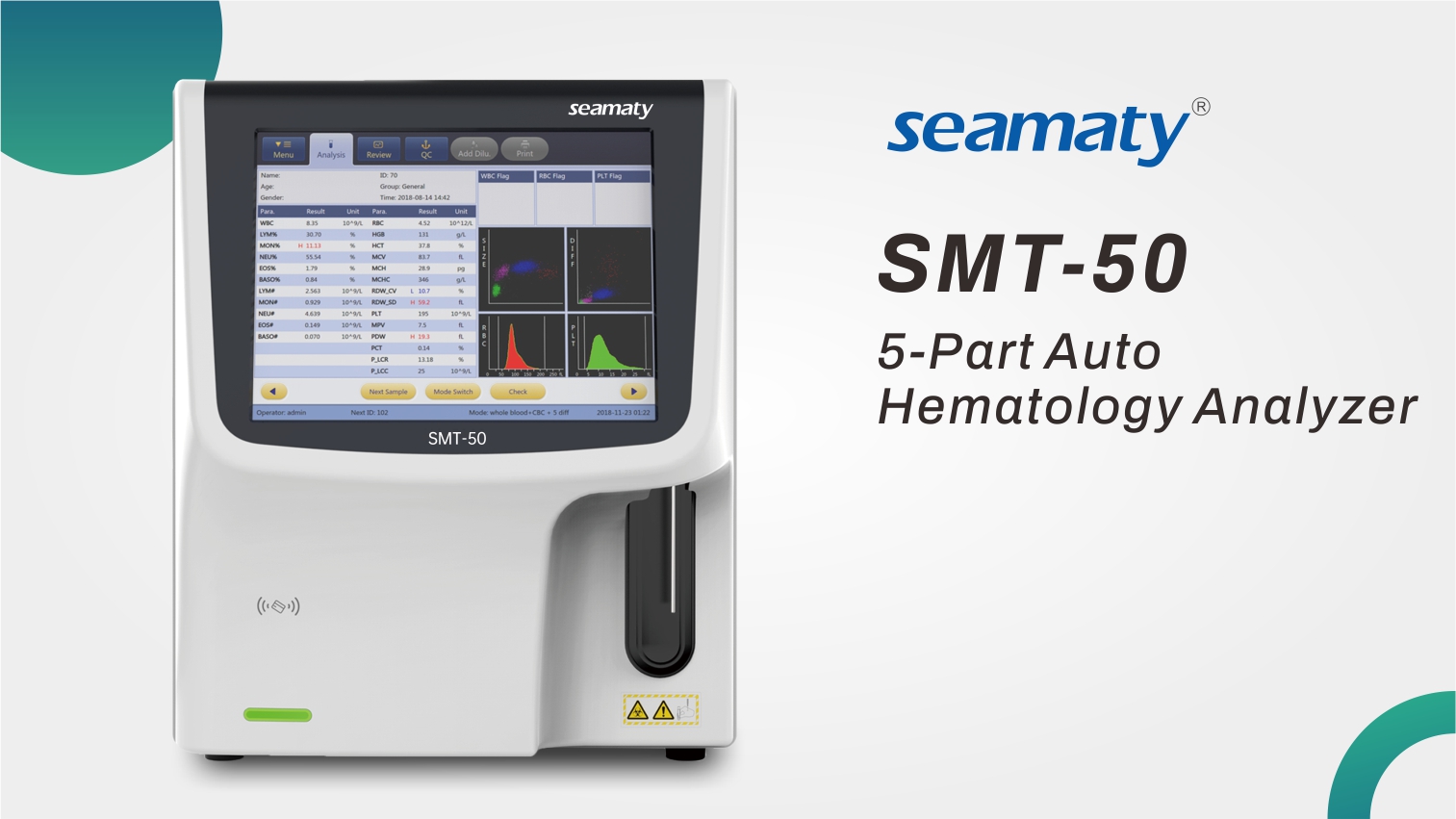
Hematology analyzer is currently the most commonly used testing instrument for clinical blood general examination. Instrument frequent use will inevitably malfunction. In addition to some relatively large failures, such as negative pressure pump into the water, peristaltic pump weakness, counting errors or not counting at all, etc. need to be repaired by the instrument manufacturer engineers. In fact, many small faults can be solved by yourself.

2021-11-11
We can simply understand POCT equipment as a new type of convenient medical equipment for examination. Its biggest characteristic is "small, fast, non-professional operation". It can be convenient for patients and reduce the time for patients to confirm the diagnosis. At the same time, POCT equipment has the function of continuous use to monitor the condition. For example, heart disease patients can quickly understand and control their condition by testing at certain intervals.
2021-10-26
Diet affects a variety of substances in the blood. For example, the concentrations of glucose (GLU), triacylglycerol (TG), ALP and phosphorus. Eating a high-protein diet one day before the blood draw can result in high urea nitrogen (BUN) and uric acid (UA) results. The increase in lipid concentrations in the blood, especially TG, after eating can lead to a milky cloudy serum, which can interfere with biochemical measurements. This may result in high results for bile acids, proteins, calcium and phosphorus. The results of amylase measurements are low.