release time:2022-04-14 17:11:52
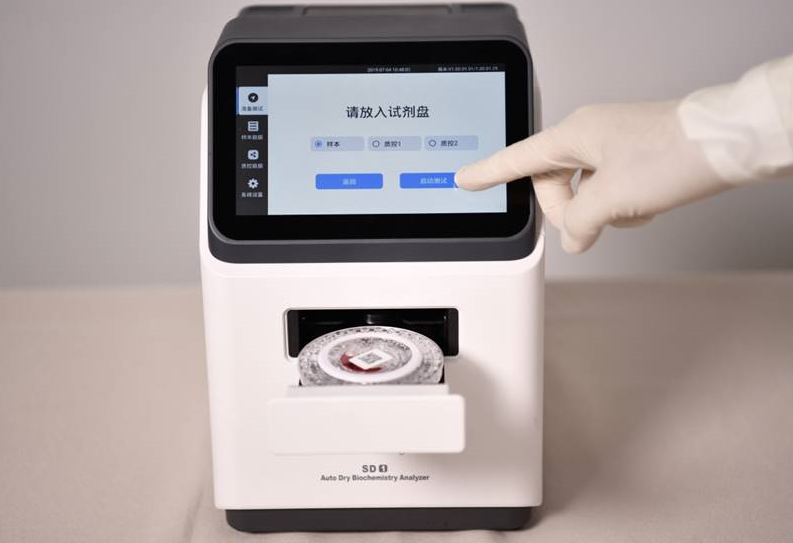
Biochemical analyzers can be simply divided into fully automatic biochemical analyzers and semi-automatic biochemical analyzers. Since most of them are now used, the following are the main components of fully automatic biochemical analyzers.
1. Sampler: place the sample to be tested, standards, quality control solution, blank solution and control solution, etc.
2. Sampling devices: including dilutors, sampling probes and pipelines for transporting samples and reagents, etc.
3. Reaction pool or reaction pipeline: generally play the role of cuvette (tube).
4. Insulator: to provide a constant temperature for the chemical reaction.
5. Detector: such as colorimeter, spectrophotometer, fluorescence spectrophotometer, flame photometer, electrochemical measuring instrument, etc.. Different instruments are configured differently.
6. Microprocessor: is the computer part of the analyzer, also known as the program controller. Control all the actions and functions of the instrument, the user can "talk" with the instrument through the keyboard, while the computer can also receive feedback from the components to the signal, and make the corresponding response to the abnormal situation issued a certain indication signal. Analysis software and analysis results are generally stored in the disk, available for query.
7. The printer: can draw reaction dynamic curve and print the test report form, etc.
8. The function of the monitor: the display is one part, you can view the reaction status, human-machine "dialogue" situation, the current instrument work status, analysis results, etc..

2022-05-07
Medical equipment is a high-risk special product directly related to personal health and safety. How to scientifically evaluate and formulate the use period of medical equipment, not only to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the product within the expiration date,
2021-11-22
1. Hemolysis: Hemolysis is one of the most common interfering factors in clinical biochemical tests. Hemolysis is the rupture of red blood cells in the blood. The contents of the red blood cells enter the serum. As a result, the concentration or activity of the biochemical test substance is affected.
2021-11-17
In the previous article we learned why animals need to do Physical exam, Blood test and Thyroid panel, what is the use of doing these tests? In addition to these tests, the Heartworm antigen test, FeLV/FIV test, Fecal exam, and X-ray are also necessary for the veterinarian to better understand the physical condition of the pet. So what is the purpose of these tests?