Biochemical testing is the earliest developed and most mature in vitro diagnostic segment. Also known as Clinical Chemistry, it is commonly used for basic tests such as blood glucose, blood lipids, cholesterol, liver function, kidney function, etc. Biochemical tests measure the levels of specific biochemical substances to determine whether the body is in a healthy state and to determine what causes them.
Biochemical testing industry development history
Since the first fully automatic biochemical instrument was introduced in 1970, the biochemical instrument industry has undergone more than 40 years of development. Biochemical testing reagents from more than 30 years ago, the situation of manual preparation, project single development to the current major enterprises no less than 100 registration certificate. New markers will keep appearing in the future, and many IVD companies are still innovating.
Biochemistry analyzer principle
Fully automatic biochemical analyzer belongs to the optical analysis instrument, the essence is equivalent to a spectrophotometer, based on the selective absorption of substances to light, that is, the spectrophotometric method. The basic measurement principle of this biochemical machine is still based on Beer's law.
The monochromator divides the complex light from the light source into monochromatic light, and the monochromatic light of a specific wavelength passes through the colorimetric cell containing the sample solution. A photoconverter converts the projected light into an electrical signal and sends it to a signal processing system for analysis. The computer then processes, calculates, analyzes and saves the measurement data according to the working mode selected by the user, and the printer prints out the corresponding results at the same time. Finally, after measuring each group of samples again for cuvette and pipeline clear.
In terms of the structure of the automatic biochemical analyzer, it includes the main components of a spectrophotometer: light source, monochromator, colorimetric cell, detector, etc..
In addition it also includes the unique parts needed for biochemical analysis, such as sample addition system, reagent system, reaction system, temperature control system, cleaning system, barcode reading system, software system, etc. It is assembled by these structures and systems together.
Types of biochemistry analyzer
Regarding the types of biochemical analyzers, there are four main classification methods as follows.
According to the degree of automation of biochemical analyzer can be divided into semi-automatic biochemical analyzer and fully automatic biochemical analyzer. At present, most hospitals basically use fully automatic biochemical analyzers.
According to the reagents and instruments can be divided into: closed system and open system. With the increasingly fierce competition in the biochemical market, many manufacturers have begun to take the closed route, which is conducive to their own market is not easy to open reagent replacement. Many mainstream biochemical analysis instrument manufacturers, the main push closed biochemical system of the instrument. At the same time they also open part of the channel.
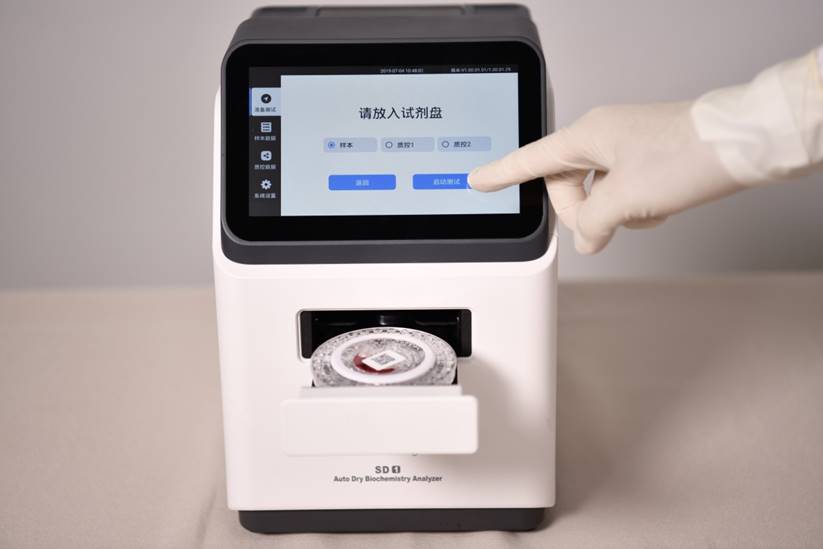
According to the biochemical analyzer reaction mode can be divided into: liquid type biochemical analyzer and dry biochemical analyzer. Most of the current market are liquid biochemical analyzers. Dry biochemical analyzers are relatively few, such as Seamaty's dry biochemical analyzer SD1, which is also very famous. Many hospitals in emergency and small laboratories use dry biochemistry.
According to the international practice of speed measurement can be divided into: small instruments and medium-sized instruments and large instruments.
-
Small biochemical analysis instruments belong to the 400 speed or less.
-
Medium-sized biochemical analyzers basically belong to the 400 speed to 1200 speed.
-
Large biochemical instruments basically belong to the 1200 speed or more, such as 1600 speed, 2000 speed.
Biochemical testing techniques and methods
The methodologies of biochemical reagents are also quite diverse. The methodologies used for different items of biochemical reagents are still largely determined by the components of the reagents and the substances involved in the reactions. Common ones such as FCC rate method, vanadate method, immunoturbidimetric method, direct method, UV endpoint method, etc. These methodologies are determined based on whether the reaction is a physical color development reaction or a chemical reaction or an antigen-antibody biological reaction. And the methodology of biochemical analyzer is basically determined, the mainstream is mainly the endpoint method, rate method, factor method.
Among the many biochemical reagent analysis methodologies, immunoturbidimetric items are also more numerous. Also immunoturbidimetric items are easily replaced by POCT as well as chemiluminescence and specific protein meters.
Such as biochemical items: homocysteine, myoglobin, troponin, cardiac fatty acid binding protein, immunoglobulin class, C-reactive protein class, rheumatoid factor, complement, pepsinogen class and so on. The methodology used for these items in the biochemical reagents is immunoturbidimetric.
Immunoturbidimetric methods for these items are also very advantageous in the field of POCT, specific protein meters, and especially chemiluminescence. Many laboratories want to carry out such projects on chemiluminescence instruments mainly based on the consideration of accurate results and performance indicators.
What can biochemistry analyzers test?
Biochemistry analyzers can currently test the following areas.
-
Liver function: ALT, AST, r-GT, ALP, T-Bil, D-Bil, TBA, TP, Alb, PA, ADA, AFU, etc.
-
Renal function: UA, UREA, Cr, β2 microglobulin, CCyst-C, UP, RBP, etc.
-
Glucose metabolism: GLU, HbA1C, FMN, etc.
-
Lipids: TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C, A1, B, aLp(a), etc.
-
Cardiac class: CK, CK-MB, LDH, α-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, MYO, IcTnI, etc.
-
Immune disease class: complement 3, complement 4, immunoglobulin A, immunoglobulin G, immunoglobulin M
-
Inflammatory response class: CRP, ASO, RF, etc.
-
Pancreatic class: AMY, PAMY, LPS, etc.
-
Electrolytes: calcium, magnesium, iron, chloride, phosphorus, carbon dioxide, etc.
-
Other classes: G6PD, etc.



