release time:2022-07-21 16:37:25
Routine blood tests are often the first step in a routine physical exam or screening for other diseases. A routine blood report usually contains many tests such as red blood cells, white blood cells, neutrophils, and so on. It can be very difficult for the average person without medical knowledge to understand the significance of the items contained in the report.
Leukocytes are the body's first barrier against infections and play a major role in immunity, and changes in leukocytes indicate changes in the body's immune system. If the number of white blood cells in the body is higher than normal, it means that there may be inflammation in the body.
To determine exactly what infection is causing the inflammation, you also need to look at the white blood cell count, neutrophil ratio and lymphocyte ratio. White blood cells are divided into 5 categories: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes.
The increase or decrease of white blood cells (WBC) is mainly influenced by neutrophils, followed by lymphocytes.
In general, bacterial infections elevate neutrophils; viral infections elevate lymphocytes; monocytes produce changes in malaria and tuberculosis infections; eosinophils are often elevated for parasitic infections; and elevated basophils are commonly seen in autoimmune diseases that attack themselves.
Each leukocyte ratio reflects the focus of the immune system's work and suggests that the immune system is strengthening a particular aspect of the immune response. Notably, when there is a tenfold or even a hundredfold fluctuation in the white blood cell count and the presence of naïve cells in the peripheral blood smear, it is often indicative of leukemia, a condition that should be given high priority.
The main function of red blood cells is to deliver oxygen to the whole body and eliminate carbon dioxide, but the function of transporting oxygen is performed by hemoglobin inside the red blood cells. The main role of hemoglobin is to bind oxygen and assist red blood cells in transporting oxygen.
If your red blood cell count, hemoglobin level and red blood cell pressure are lower than normal, you are likely to have anemia. Anemia can cause discomfort such as weakness, dizziness and heart palpitations and panic.
Platelets are small pieces of cytoplasm that are shed from the cytoplasm of mature megakaryocytes in the bone marrow and are the smallest cellular component of the blood. Its function is mainly to promote hemostasis and accelerate clotting, and to maintain capillary wall integrity.
Too many or too few platelets can cause abnormal coagulation, and doctors generally analyze the cause of the disease in terms of insufficient production, excessive consumption, and increased destruction.

2022-09-18
Common biochemistry analyzers are divided into semi-automatic and fully automatic biochemistry analyzers based on the degree of instrument intelligence. Compared to fully automatic biochemistry analyzers, semi-automatic biochemistry analyzers are more compact, simple in structure, and more versatile in use scenarios.
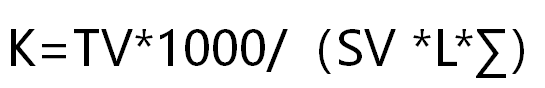
2022-05-16
The calibration of a biochemistry analyzer is to find a reference point, which is to determine a K value (or F value). It is determined by the state of the instrument and reagents.

2022-04-15
Biochemical testing is one of the important tools commonly used in clinical diagnosis. At present, dry chemistry (biochemical) analyzers have also been more widely used. What is a dry biochemistry analyzer? How to use this biochemical machine?