release time:2022-10-11 13:55:29
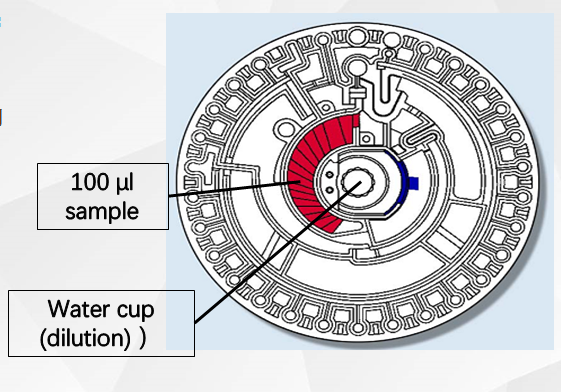
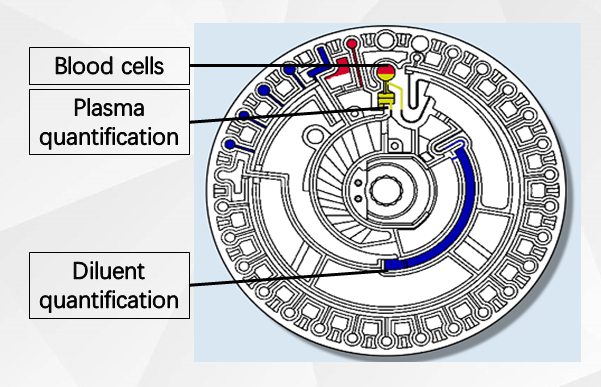
The biochemistry machine's built-in motor drives the test disc at high speed. Under the action of centrifugal force, the sample and diluent move towards the periphery away from the center of the test disc (built-in centrifugation).
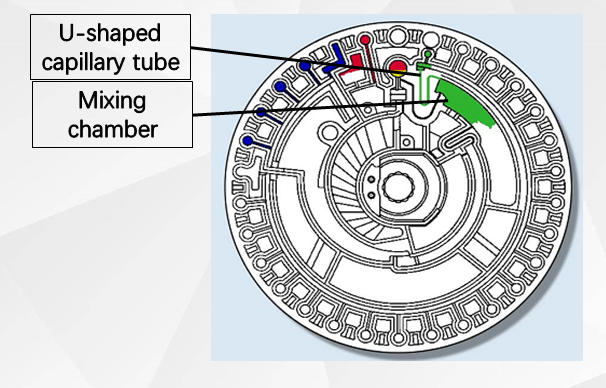
Under the alternating action of the siphoning force of the capillary and the centrifugal force, the sample and diluent after the fixed volume enter the mixing chamber. The biochemistry machine uses alternating acceleration and deceleration movements to mix the sample and diluent homogeneously.

2022-07-06
A clinical chemistry analyzer is a machine used to perform chemical analyses of various samples, including blood and urine. Chemistry analyzers are an important part of many clinical laboratories,

2021-09-09
Biochemical analysis is one of the most important tools commonly used for clinical diagnosis. Biochemical analysis can be divided into wet chemistry and dry chemistry according to whether the chemical reaction between the sample and the reagents is in solid phase or not.
2021-09-02
Biochemistry is able to test total cholesterol (CHO), triglyceride (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and other items related to blood lipids. The biochemistry analyzer enables an all-round understanding of blood lipid levels with accuracy and credibility.