release time:2022-10-11 13:17:00


The current mainstream discrete automatic biochemistry analyzers can be programmed in the same way as manual operation. And a rhythmic mechanical operation is used instead of manual. Each link is connected with transfer belt and operated sequentially. The biggest advantage of this instrument is its speed, low cross-contamination and many test items.
Wet chemistry is an ordinary chemical reaction. It is a chemical reaction that occurs when liquid reagents and samples are added to the reaction vessel and mixed. Dry chemistry is the opposite. Dry chemistry uses a solid phase reagent technique with multilayer films. The liquid sample is simply added directly to a reagent carrier that has been solidified in a special structure, i.e., dry chemistry. The water in the sample is used as a solvent to dissolve the reagents cured in the carrier and then chemically react with the components to be measured in the sample. Thus, the analytical determination is performed.
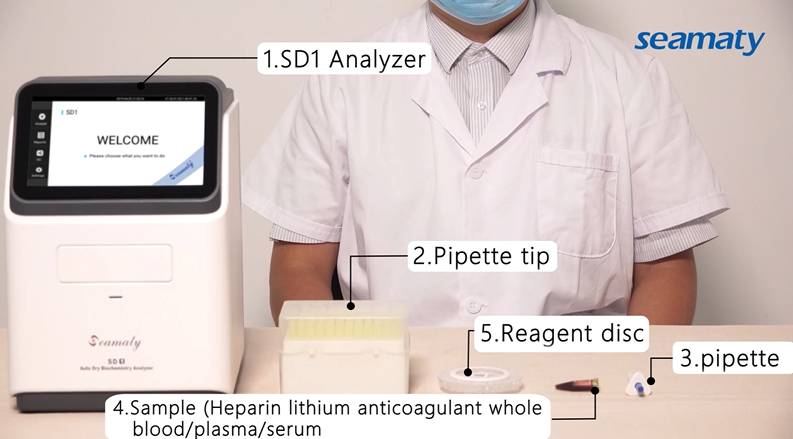
Dry biochemical analyzer, because of its rapid test, simple operation and accurate results, can be used for biochemical testing in a variety of settings. These biochemistry machines are generally used for POCT. the instruments are small in size and can produce blood test reports in ten minutes. They are widely used in small hospitals, outpatient and emergency departments of large and medium-sized hospitals, medical examination centers, community, rural and other primary health care institutions.

2022-09-29
A CBC test machine is a type of medical equipment that is used to measure the levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in a person's blood. This information is important in order to diagnose and treat various medical conditions.

2022-04-25
Does high uric acid necessarily cause gout? What are the specific dangers? And how should we prevent and treat it?

2022-01-25
Here are some examples of test instruments commonly used in medical testing laboratories, some very basic consumables and supporting equipment. Hope to help you buy laboratory equipment.